Spark Protocol: An Overview
1/13/2024
Overview
The Spark Protocol was originally created by MakerDAO as a way to proliferate DAI and increase the use cases of their multi-asset backed stablecoin. The protocol currently offers three flagship products: SparkLend, sDAI and SparkConduits.
SparkLend
SparkLend is a DAI centric money market platform, that uses a credit line from Maker called a Dai Direct Deposit Module (D3M). SparkLend is designed to leverage Maker’s substantial liquidity and real-world asset revenue to create an efficient borrow and lend platform, whilst also generating cashflow for MakerDAO . With the permission of the Aave team, the codebase was forked from Aave V3. In return the Spark protocol has agreed to pay Aave 10% of all the profits made within the DAI protocol.
Similar to most lending protocols, Spark enables users to deposit assets as collateral and borrow against them. A distinctive feature of Spark is its role in MakerDAO’s endgame, being the first SubDAO of MakerDAO.
sDAI, DSR and EDSR
Dai Savings Rate (DSR): The DSR is a feature within the Maker Protocol allowing DAI holders to earn yield on their DAI. The DSR acts as peg support and a monetary policy tool to control DAI supply.
sDAI: sDAI is an ERC-4626 representation of DAI, that distributes MakerDAO revenue as yield to DAI holders who place their DAI in this module / vault. It allows users to earn yields from the Maker protocol on their DAI deposits, while retaining the flexibility to transfer, stake, lend, or use their DAI. Conversion between DAI and sDAI doesn’t require a DEX but is managed through deposits and withdrawals from the DSR module, with platforms like SparkLend offering a user interface for interacting with sDAI.
Enhanced Dai Savings Rate (EDSR): EDSR is a temporary enhancement to the DSR, designed to boost the effective DSR during its initial stages, when usage is low. The yield is determined by the DSR’s utilization rate (i.e. it depends on the percent of DAI supply is in the DSR). The ESDR yield decreases as usage increases and disappears at high utilization levels (more DAI in the DSR). EDSR only decreases over time and doesn’t impact other parameters like stability fees, which are based solely on the underlying DSR.

SparkConduits
SparkConduits allow for direct liquidity to flow from Maker to other protocols as part of the overall Maker Allocation System, by facilitating the movement of funds between the Maker Allocation System and the SparkLend protocol, and by calculating the interest rate that is paid by all borrowers of DAI through the SparkLend protocol.
Spark and Endgame
Spark Protocol launched to address MakerDAO’s struggle in scaling. Expanding horizontally into other sectors such as lending or derivatives under a single DAO’s governance is complex. To address this, the Maker team introduced its “Endgame” plan to enhance the efficiency of the Maker system.
Spark, as a SubDAO, functions primarily as an AllocatorDAO. It specializes in allocating DAI (and later on NewStable, Maker’s upcoming, new DAI-like stablecoin, set to replace DAI) collateral. The goal for Allocator SubDAOs are to manage DAI collateral through Allocator Vaults, eliminating the need for native vaults, PSMs, and more. Only the Sagittarius Lockstake Engine remains as a native vault for long-term MKR holders to generate Dai.
As of January 12 2024, Spark has $2.015B USD in total value locked, and $1.179B USD in total value borrowed.

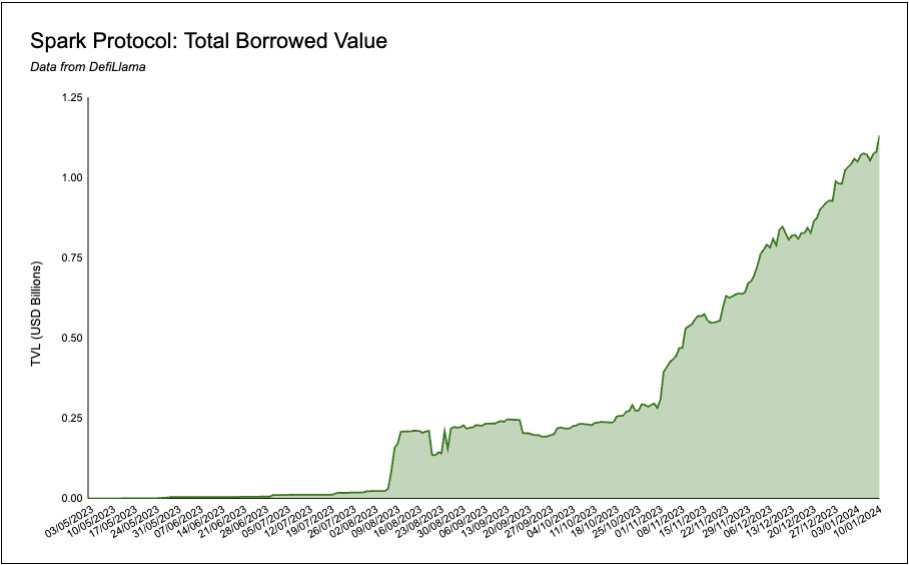
Mechanics
Users can deposit their assets on Spark Protocol and borrow others as needed. However, Spark introduces unique features (some from Aave V3):
E-mode (High Efficiency Mode): This mode increases capital efficiency for assets with correlated prices, such as stablecoins pegged to the USD (e.g., sDAI, USDC, USDT). Users supplying assets like sDAI in E-mode can borrow other assets from the same category with enhanced collateralization power. E-mode restricts borrowing to assets within the same category, but it does not limit the use of other assets as collateral.
Isolated Mode: Implemented by Maker Governance, this mode allows the listing of new assets with a specific debt ceiling. Only certain approved stablecoins can be borrowed under this mode, with the approval of these assets determined by MKR token holder votes.
sDAI: Spark has integrated the DAI Savings Rate (DSR) module. sDAI is a wrapper of DAI within this module, allowing users to convert DAI to sDAI directly on Spark.
Assets Available for Borrowing
Users can supply and borrow a variety of assets, including DAI, GNO, rETH, sDAI, USDC, USDT, WETH, and wstETH.
Liquidation Mechanism
Liquidation occurs when a borrower’s Health Factor (HF) reaches 1, indicating their collateral value is insufficient to cover their loan. Upon liquidation, up to 50% of the debt must be repaid, with a bonus or penalty claimable by the liquidator. The liquidated amount and bonus are deducted from the available collateral. In scenarios with multiple collateral types, liquidators can choose different bonus rates for different assets, prompting competition among professional DeFi users to capture these bonuses. To avoid liquidation, users should deposit more assets or repay their loans in advance.
Tokenomics of Spark Protocol
The specifics of the SPK tokenomics are yet to be released. SPK is expected to launch alongside SparkDAO in May 2024, and as the governance token for SparkDAO. The token launch will feature a pre-farming airdrop, rewarding borrowers who use volatile assets as collateral. Following this, a genesis farming period will distribute 2 billion SubDAO tokens over ten years, with a focus on NS (NewStable) holders and staked NGT (NewGovernanceToken) holders. The distribution is as follows:
Years 1-2: $500 million per year ($350 million for NS/$150 million for NGT)
Years 3-4: $250 million per year ($175 million for NS/$75 million for NGT)
Years 5-6: $125 million per year ($87.5 million for NS/$37.5 million for NGT)
Years 7-10: $62.5 million per year ($43.75 million for NS/$18.75 million for NGT)
The reward ratio for NS and NGT is 70%:30%. Post-Genesis farming, there will be a permanent emission of 10% of tokens per year across various allocations.
It’s important to note that, due to its affiliation with Aave, 10% of Spark’s gross profits are allocated to the Aave Treasury, a proposal that was ratified via Snapshot eight months ago.
Spark Strategies
A popular strategy amongst depositors has been to deposit assets like ETH or LSTs, and borrow against them with DAI. Depositors then convert the DAI to sDAI to capitalize on the DSR and earn 5% yield, or they deposit the DAI back into the protocol and borrow WETH or LSTs, to loop and lever up.

A good example of this LST looping strategy is the 7 Siblings wallet. This $1.7B AUM wallet is currently lending nearly 80K ETH (worth approximately $208M USD) in the Spark Protocol, and borrowing 90.9M units of DAI against it. This strategy allows 7 Siblings to get low-level leverage on their passive ETH holdings, whilst also farming the SPK airdrop.

Likewise, 0xaa is utilising his passive ETH & stETH holders in order to borrow DAI. With stETH 0xaa is getting the ETH staking yield on top of his net borrow/lend yield, whilst also farming the upcoming token.

Another common strategy is the inclusion of Maker’s Dai Savings Rate module. 0x8af lends both ETH and stETH, borrowing DAI on moderate leverage. With approximately half of the borrowed DAI, 0x8af places this in the DSR earning a 5% APR.
Disclaimer:
The information and services above are not intended to and shall not be used as investment advice.
You should consult with financial advisors before acting on any of the information and services. ASXN and ASXN staff are not investment advisors, do not represent or advise clients in any matter and are not bound by the professional responsibilities and duties of a financial advisor.
Nothing in the information and service, nor any receipt or use of such information or services, shall be construed or relied on as advertising or soliciting to provide any financial services.